Understanding DeFi Vaults: Infrastructure, Execution, and Strategy
Jul 4 | 5 Mins MIN | Product

By
Kvants
Smart Contract Architecture and Capital Routing
DeFi vaults are autonomous smart contract systems that manage digital asset allocations across various DeFi protocols. Unlike basic staking contracts or liquidity pools, which statically hold user deposits, vaults are programmed with strategy logic that governs how assets are deployed, when they are rebalanced, and under what conditions trades are executed. At the architectural level, vaults consist of three key components: the asset pool (where deposits are held), the controller (which oversees strategy logic), and the execution module (which interacts with external DeFi protocols).
Yield Generation Strategies for Vaults
This modular design allows vaults to operate as non-custodial, composable financial engines. Users deposit capital, commonly stablecoins or volatile tokens into a vault and receive vault tokens representing a share of total NAV. The smart contract autonomously routes these deposits into yield-generating strategies such as liquidity provision, lending markets, or arbitrage loops. Vaults track every transaction and adjustment through on-chain events, offering complete transparency into allocation behavior. Some vaults also integrate Layer 2 automation or off-chain data to trigger events based on price feeds or funding rates. This dynamic, rules-based infrastructure enables vaults to abstract away the complexity of DeFi’s multi-protocol environment while delivering automated yield extraction to end users.
Yield Strategy Design and Risk Management
The core differentiator of DeFi vaults lies in their strategy execution. Simple yield strategies might involve depositing stablecoins into lending markets like Aave or Compound to earn base rates, while more complex strategies incorporate leverage, derivatives, or cross-market arbitrage. One commonly implemented model is delta-neutral trading, where the vault enters a long spot position and simultaneously shorts a perp contract, maintaining minimal net exposure to price movements. These positions are algorithmically rebalanced in real-time to maintain risk thresholds, particularly during volatile market regimes. Vaults encode protective logic such as Value-at-Risk (VaR) limits, leverage caps, and conditional stop-losses that trigger based on slippage, oracle divergence, or liquidity availability.
Smart Contracts and Autonomous Execution
Each risk module is embedded into the smart contract and executed autonomously. Users interact only with the vault interface, unaware of the underlying complexity. In cases where market structure or strategy assumptions shift, vaults can pause, rebalance, or withdraw to safety modes without user intervention. This eliminates manual oversight and central operator risk. Additionally, audits and formal verification processes are critical for trust, given vaults manage pooled capital across complex strategies. Together, the design and risk mechanics of vaults allow them to function as autonomous hedge fund-like products, accessible on-chain through a few clicks.
Execution Infrastructure and Composability
DeFi vaults are not isolated products; they are increasingly composable primitives in the broader decentralized finance stack. Most are built using ERC-4626 or equivalent token standards, which allows them to integrate with lending protocols, liquidity aggregators, and structured product platforms. This tokenization of vault shares enables them to be used as collateral, LP positions, or rehypothecated in multi-layer DeFi strategies. On-chain execution is typically triggered through condition monitoring systems that track funding rate spreads, volatility shifts, or portfolio imbalance thresholds. In Solana-based vaults, execution speed and gas efficiency become enablers for high-frequency updates, especially for momentum or stat arb strategies.
Drift-integrated Vaults
Drift-integrated vaults, for instance, can open and close perp positions directly within the same block that rebalances their hedge exposure, minimizing latency. Moreover, oracles like Pyth and Switchboard provide reliable price inputs for rebalancing triggers, while execution optimizers route trades to reduce slippage. Some vault systems are also integrating AI-driven signal layers that pre-process trade signals before execution, improving edge capture. In essence, DeFi vaults represent programmable capital autonomously reallocated across permissionless venues without centralized control. Their execution logic, encoded within immutable contracts, eliminates discretionary behavior and standardizes DeFi participation at institutional-grade precision.
The Future of DeFi Vaults and Digital Asset Allocation
As DeFi matures, vaults are evolving from yield wrappers into full-spectrum digital asset managers. The trend is clear: platforms are moving beyond simple auto-compounding to deploying multi-strategy quant infrastructure on-chain. Vaults are beginning to mirror the architecture of traditional fund management, complete with performance attribution, on-chain accounting, and parameterized governance. With the proliferation of derivatives, synthetic assets, and tokenized RWAs, vaults can serve as allocation engines across not only crypto markets but real-world asset exposure. We are also seeing vault strategies increasingly tailored to market regimes momentum vaults during high volatility, carry vaults during sideway trends, and mean-reversion vaults in statistical arbitrage setups.
Programmable Asset with Defi Vaults
Modular design further allows users or DAOs to select vaults that match their portfolio risk parameters, time horizon, and exposure profile. Future iterations may introduce zk-enabled privacy vaults, real-time auditing layers, and composable vault-of-vault architectures that layer strategies into meta-portfolios. As compliance, transparency, and risk frameworks mature alongside smart contract infrastructure, vaults may become the default gateway for capital into digital asset markets, removing the technical barriers and trust dependencies currently slowing adoption. In this sense, DeFi vaults are not only tools for yield they are programmable asset managers designed for scale.
Security Considerations and Oracle Dependencies
While DeFi vaults offer structured automation, they are highly sensitive to security risks and data reliability. The immutability of smart contracts makes pre-deployment auditing essential, as any exploit or misconfiguration can result in irreversible asset loss. Security audits must encompass not only vault logic but also its dependencies, external contracts, price oracles, and composability layers. Vaults often rely on oracle feeds to monitor conditions like price thresholds, funding rate differentials, or asset weightings. If oracle feeds are manipulated or diverge significantly, it may lead to incorrect execution logic, triggering trades or rebalances under false conditions.
Upgradeability of Defi Vault Contracts
Protocols like Chainlink, Pyth, and Switchboard are now integral to robust vault deployment. Additionally, the upgradeability of vault contracts poses a trade-off between flexibility and trust minimization. Timelocks, multisigs, and decentralized governance processes are often introduced to balance these concerns. Vaults must also account for economic attack vectors, sandwich attacks, MEV extraction, or front-running especially for strategies that rely on narrow arbitrage windows. Ultimately, trust in a vault stems from the transparency of its security architecture, including how it monitors contract health, responds to edge cases, and verifies strategy integrity. As vaults scale in TVL and complexity, the emphasis on modular risk segmentation and real-time circuit breakers will only grow.
Use Cases Beyond Yield: Structured Products and Treasury Management
DeFi vaults are increasingly serving as vehicles for more than passive income. In institutional contexts, they function as structured products that offer tailored risk-return profiles, often embedded with derivatives or custom logic. For DAOs and treasury managers, vaults provide automated capital deployment that aligns with governance mandates allocating idle assets into low-risk lending vaults or high-conviction directional strategies. Custom vaults can mirror payout profiles of traditional structured notes, including downside protection, capped upside, or conditional triggers based on oracle feeds. Additionally, vault tokens themselves can be used in liquidity mining campaigns, governance staking, or collateralization frameworks.
The Versatility of Defi Vaults
In multi-chain environments, vaults may abstract execution across Layer 2s or sidechains, allowing capital to chase yield opportunities across fragmented ecosystems without active management. For market makers, vaults provide delta-hedged exposure with real-time position visibility and automated rebalancing. For retail users, they simplify participation by encapsulating complexity behind a single deposit action. The versatility of vaults continues to expand with the development of new strategy templates, contract standards, and composable middleware. As vault infrastructure matures, it’s likely they will underpin the next generation of DeFi primitives, shaping not just yield aggregation, but the architecture of decentralized asset allocation at scale.
Kvants Vaults and Systematic Strategy Deployment
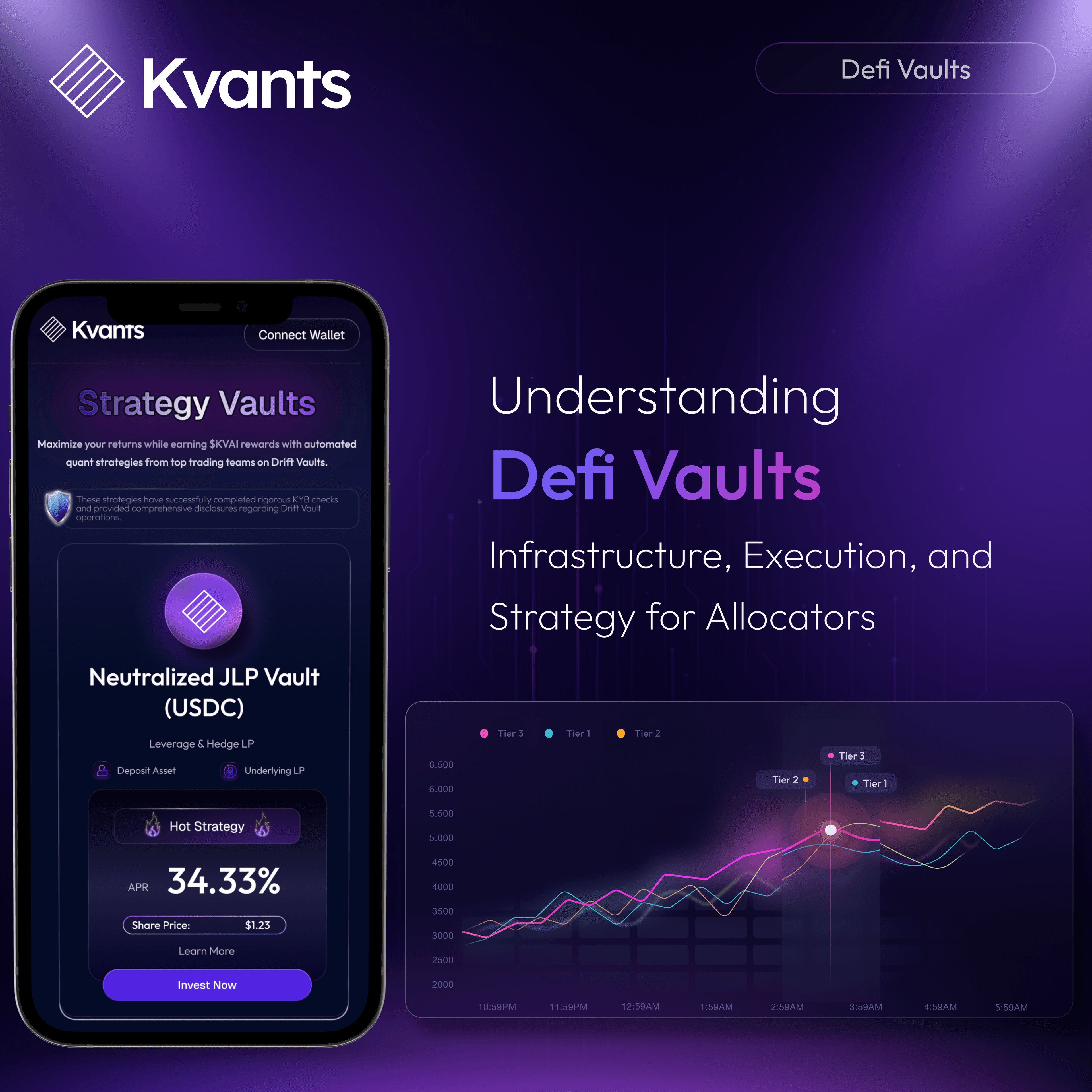
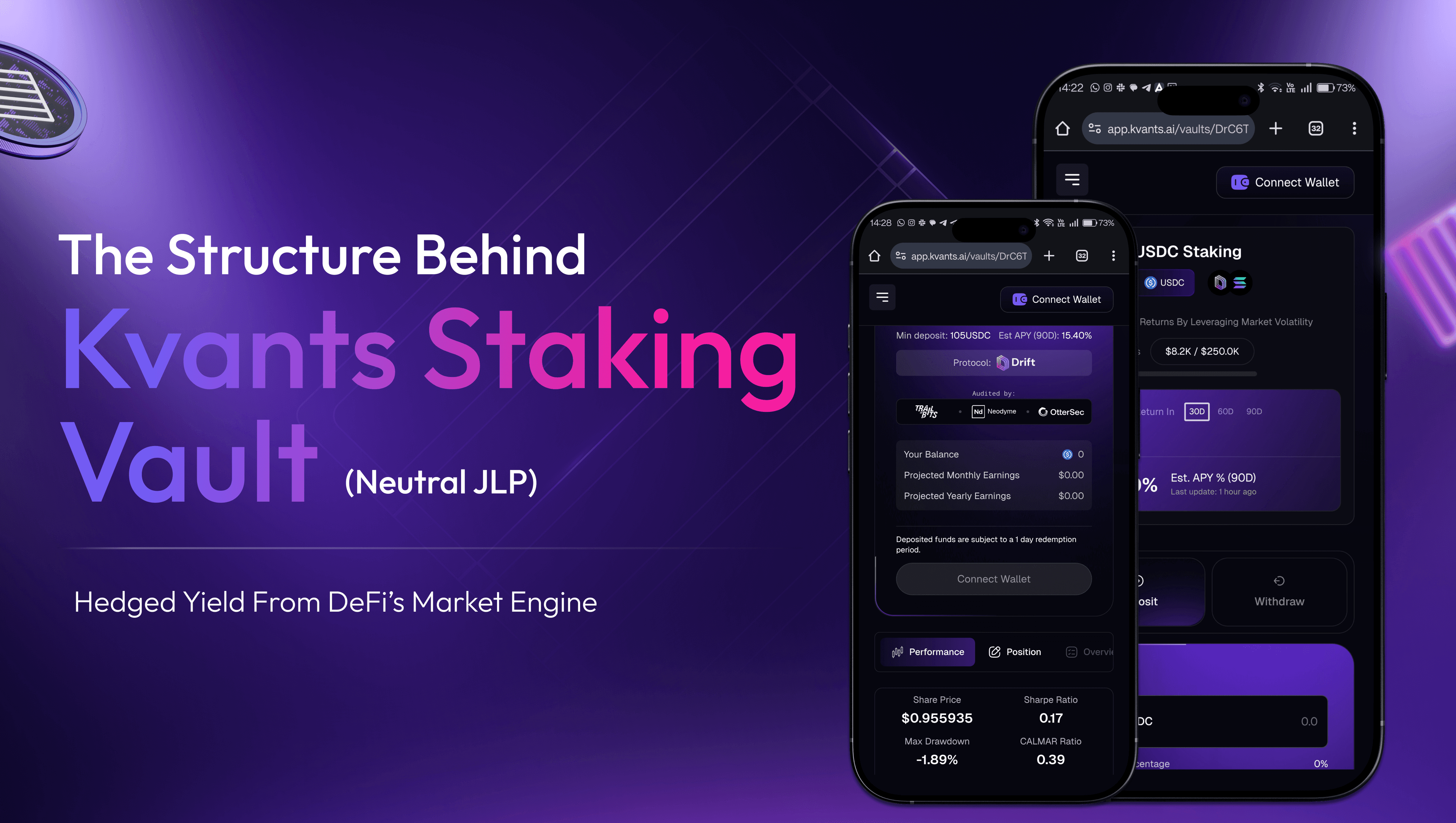
A notable example of this evolution is the Kvants Vault suite on-chain smart contract systems that deploy quantitative trading strategies with deterministic execution logic. Kvants integrates deeply with Drift protocol on Solana, enabling vaults to enter positions directly into perps and spot markets within the same execution environment. Their strategies include delta-neutral funding-rate carry, statistical arbitrage, short-term momentum, and neutralized JLP yield, each encoded with real-time risk controls such as Value-at-Risk ceilings, hedge ratio enforcement, and automated stop-loss modules.
institutional-grade Vault Infrastructure
Kvants vaults ingest real-time data from oracles like Pyth and execution signals from proprietary off-chain models, and route trades directly via smart contracts, ensuring transparency, precision, and zero reliance on off-chain actors. Vault users retain full custody of their funds, and every trade, rebalance, and parameter update is verifiable on-chain. The result is an institutional-grade vault infrastructure that abstracts away strategy execution complexity while providing stablecoin-denominated returns with transparent, programmable logic. Kvants illustrates how DeFi vaults can evolve into modular asset managers, delivering diversified and strategy-specific alpha with the composability and transparency that DeFi was built to provide.
Final Thoughts
DeFi vaults are evolving into programmable financial infrastructure, built to handle execution, risk, and strategy in a fully autonomous way. As vaults grow more sophisticated, the opportunity to automate capital deployment at scale is becoming a reality. Products like Kvants Vaults are showing how strategy, security, and transparency can be encoded natively on-chain. Kvants is is fast becoming a core layer of digital asset management.

Read more